Any diseases related to reproductive organ deduction and treatment
Any disease or disorder that affects the human reproductive system is referred to as a reproductive system disease. They include abnormal hormone production by the ovaries or testes, as well as abnormal hormone production by other endocrine glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, or adrenal glands. Such diseases can be caused by genetic or congenital abnormalities, infections, tumors, or disorders of unknown origin.
Genetic and congenital abnormalities in male
Severe penis anomalies are uncommon and are usually associated with urinary or other systemic defects that make life impossible. Anomalies of the penis include absence, transposition, torsion, and duplication. An abnormally large penis is often seen in men who have precocious puberty, dwarfism, an overactive pituitary, or adrenal tumors.
Small penises are seen in infantilism, genital underdevelopment, pituitary or pineal gland under secretion, and failure of corpora cavernosa development.
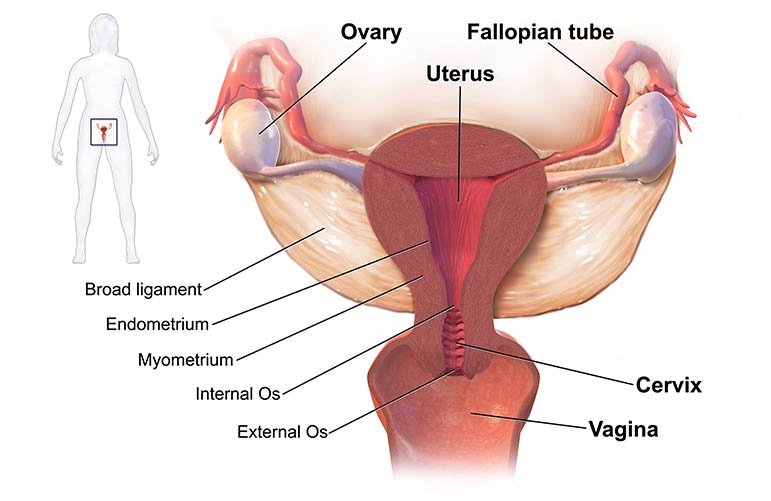
Genetic and congenital abnormalities in female
Female external genitalia is less complex than male external genitalia, but they do have anomalies that can interfere with the functioning of the female urogenital tract. The clitoris, an erectile structure similar to the penis except that it does not contain the urethra, may be absent or enlarged due to congenital or hormonal factors.
Vaginal and uterine anomalies include complete absence, incomplete development, and duplication. Women's urethras may have a narrow opening, known as a meatus, be distended, have an abnormal pouch in their wall, known as a diverticulum, or open abnormally into the vaginal cavity.
