Reproductive Tract Infection
Reproductive tract infection is also known as Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID). It occurs when the female reproductive organs become infected. This part of the body is responsible for pregnancy and childbirth.
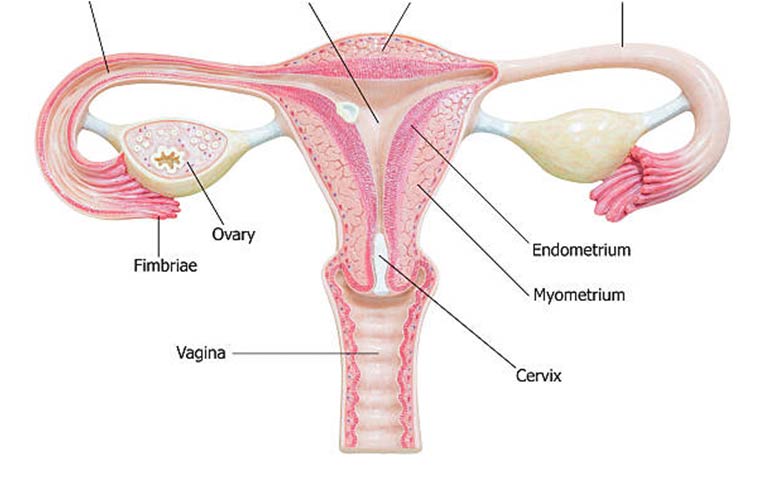
PID affects reproductive organs such as the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. You may experience stomach pain in your lower abdomen if you have PID. You may also experience unusual vaginal discharge.
The majority of people contract PID through unprotected sex, but 15% of these infections are not transmitted sexually. Sex can allow bacteria to enter the reproductive system and infect the organs. PID can harm reproductive organs such as the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. PID can be painful and make future pregnancy more difficult. PID can also cause a pocket of infection in the pelvis known as a tube-ovarian abscess, which can be fatal if left untreated.
Symptoms and causes
Symptoms of reproductive tract infection
- The most common symptom is pain or tenderness in the stomach or lower abdomen
- Vaginal discharge that is abnormally yellow or green and has an unusual odor.
- Fever or chills
- Vomiting and nausea
- Pain while having sex
- Peeing causes burning.
- Period irregularity, spotting or cramping throughout the month
- Pain in the right upper abdomen
Causes
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvis are frequently caused by bacteria entering the reproductive tract. These bacteria travel from the vagina to the cervix, then into the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and finally into the pelvis.
When bacteria enter the vagina, the cervix normally prevents them from spreading to other reproductive organs. However, the cervix can become infected with an STI such as gonorrhea or chlamydia. When this happens, it becomes less effective at keeping bacteria out.
Other common causes include:
- Abortion
- Childbirth
- Pelvic surgery
- Insertion of a copper or hormonal intrauterine device
