Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
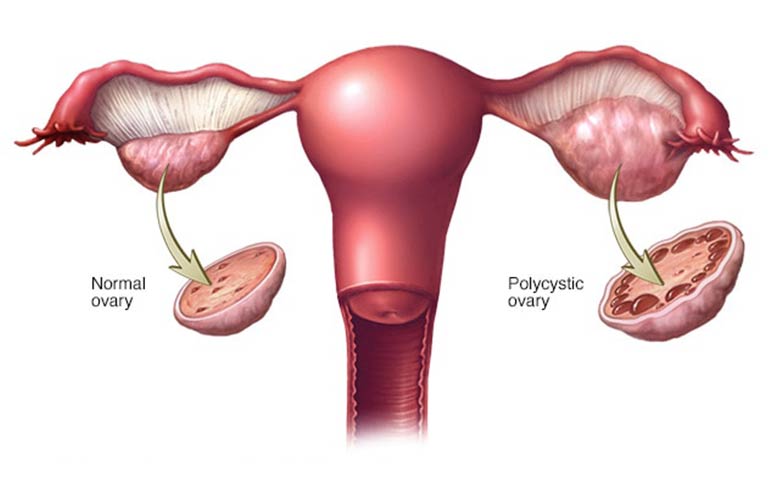
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal condition that affects many women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have irregular or prolonged menstrual cycles, as well as high levels of male hormones. The ovaries may develop a large number of small collections of fluid (follicles) and fail to release eggs on a regular basis.
PCOS's exact cause is unknown. Early detection and treatment, as well as weight loss, may lower the risk of long-term complications like type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
PCOS Signs and Symptoms
PCOS symptoms frequently appear around the time of the first menstrual period during puberty. PCOS can develop later in life, for example, as a result of significant weight gain.
PCOS symptoms and signs vary. When you have at least two of the following symptoms, you have PCOS.
Irregular periods: The most common symptom of PCOS is infrequent, irregular, or prolonged menstrual cycles. For instance, you could have fewer than nine periods per year, more than 35 days between periods, or abnormally heavy periods.
High Androgen levels of male hormones can cause physical symptoms such as excess facial and body hair (hirsutism), severe acne, and male-pattern baldness.
Polycystic ovaries: Your ovaries might be enlarged and contain follicles that surround them.
